Sharing China-Made with Global Customers

When choosing the right material for your project, understanding the differences between carbon steel vs alloy steel is crucial. Both types of steel have unique properties that make them suitable for various applications. In this guide, we’ll explore their compositions, strengths, weaknesses, and common uses to help you make an informed decision.
Carbon steel is primarily composed of iron and carbon, with trace amounts of other elements. The carbon content typically ranges from 0.05% to 2.0%, significantly influencing the steel’s hardness and strength.
· Low Carbon Steel (Mild Steel): Contains up to 0.3% carbon. It’s ductile, weldable, and commonly used in construction and automotive bodies.
· Medium Carbon Steel: Contains 0.3% to 0.6% carbon, offering a balance of strength and ductility. Used in gears, axles, and machinery parts.
· High Carbon Steel: Contains 0.6% to 2.0% carbon, making it extremely hard but brittle. Ideal for cutting tools, knives, and springs.
✔ High strength and durability
✔ Cost-effective compared to alloy steel
✔ Excellent machinability and weldability
✖ Prone to corrosion (unless coated or treated)
✖ Less resistant to extreme temperatures
Alloy steel is enhanced with additional elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, or vanadium to improve specific properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and heat tolerance.
· Low Alloy Steel: Contains small amounts of alloying elements (up to 8%), improving hardness and toughness. Used in pipelines and structural components.
· High Alloy Steel: Contains significant amounts of alloying elements (over 8%), such as stainless steel (chromium-rich) for superior corrosion resistance.
✔ Enhanced strength and toughness
✔ Better corrosion and heat resistance
✔ Customizable properties based on alloying elements
✖ More expensive than carbon steel
✖ Can be harder to machine and weld
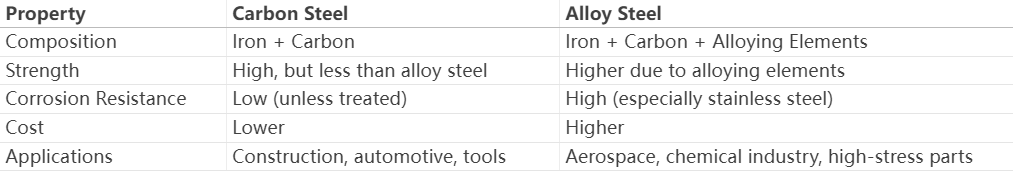
The choice between carbon steel vs alloy steel depends on your project requirements:
· Choose carbon steel if you need a cost-effective, strong material for general construction or machinery.
· Choose alloy steel if you require enhanced properties like corrosion resistance, heat tolerance, or high strength for specialized applications.
Both carbon steel and alloy steel have distinct advantages depending on the application. Carbon steel is ideal for budget-friendly, high-strength needs, while alloy steel offers superior performance in demanding environments. By understanding their differences, you can select the best material for your project.
For more insights on steel types and their applications, stay tuned to our blog!