Vision/Value: Pragmatism, Integrity, Passion

When selecting steel pipes for industrial applications, the debate between spiral welded pipe vs longitudinal welded pipe is crucial. Both types serve different purposes based on their manufacturing processes, structural integrity, and performance under pressure. This guide explores their key differences, advantages, disadvantages, and best-use cases to help you make an informed decision.
· Produced by helical (spiral) welding, where a steel strip is coiled at an angle and continuously welded along its length.
· Uses Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) for high-strength, large-diameter pipes.
· Ideal for pipes with diameters ranging from 20 inches to over 100 inches.
· The spiral seam provides uniform stress distribution along the pipe’s length.
· Manufactured by bending a steel plate and welding it straight along its length (longitudinally).
· Common welding methods:
o ERW (Electric Resistance Welding) – For smaller pipes.
o LSAW (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welding) – For thicker, high-pressure pipes.
o HFW (High-Frequency Welding) – For precision welding.
· Best suited for small to medium diameters (up to 24 inches).
Key Takeaway:
· Spiral welded pipe vs longitudinal welded pipe differs primarily in seam orientation—helical vs straight.
· Spiral welding allows for larger diameters, while longitudinal welding is better for high-pressure applications.

· Spiral welds distribute stress more evenly, making them ideal for piling and structural applications.
· Longitudinal welds provide higher burst strength, preferred for oil & gas pipelines.
✔ Water & Sewage Systems – Cost-effective for large-diameter pipelines.
✔ Piling & Foundations – High flexibility and stress resistance.
✔ Low-Pressure Oil & Gas Transport – Suitable for non-critical lines.
✔ High-Pressure Pipelines – Oil, gas, and petrochemical industries.
✔ Mechanical & Automotive Tubing – Precision welding required.
✔ Construction & Scaffolding – Strong, straight-seam reliability.
Spiral welded pipe vs longitudinal welded pipe selection depends on diameter, pressure requirements, and budget.
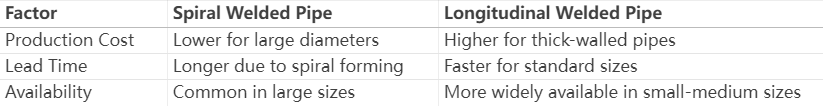
· Spiral welded pipes are cheaper for large-scale projects (e.g., water mains).
· Longitudinal pipes are more cost-effective for high-pressure, precision applications.
· Weld defects can occur due to the helical seam.
· Not ideal for high-pressure applications.
· Thicker walls required for equivalent strength vs longitudinal.
· Limited to smaller diameters (usually under 24 inches).
· Straight seam creates stress points, making them less flexible.
✅ You need large diameters (20+ inches).
✅ Your project requires even stress distribution (e.g., piling).
✅ Budget is a concern for low-medium pressure systems.
✅ You require high-pressure resistance (e.g., oil & gas).
✅ Precision welding is critical (e.g., automotive tubing).
✅ You need faster production for standard sizes.
The spiral welded pipe vs longitudinal welded pipe debate comes down to application requirements.
· Spiral welding is best for large, low-pressure systems.
· Longitudinal welding excels in high-pressure, precision-demanding environments.
Need expert guidance? Contact us for the best welded pipe solutions tailored to your project!